Managing DAG Dependencies in Airflow
Overview
All Airflow DAGs internally possess a Cron object, which is used to establish dependencies between them. However, dependencies were previously limited to the following pairs:
Upstream <> Downstream
- daily cron <> day-of-week cron
- daily cron <> daily cron
- hourly cron <> hourly cron
Recently, a lack of dependency settings between a daily cron and an hourly cron for our team led to an issue where the hourly cron job started before the daily cron job had finished. To resolve this, I have implemented logic to automate the configuration of dependencies between any cron objects.
Preliminary
What is a logical date?
Consider a job with the following Cron schedule:
"0 0 * * *" # Everyday at 00:00
This cron schedule can be visualized as follows. (Since Airflow internally manages a schedule with a start, end, and interval, I have represented it as a box.)
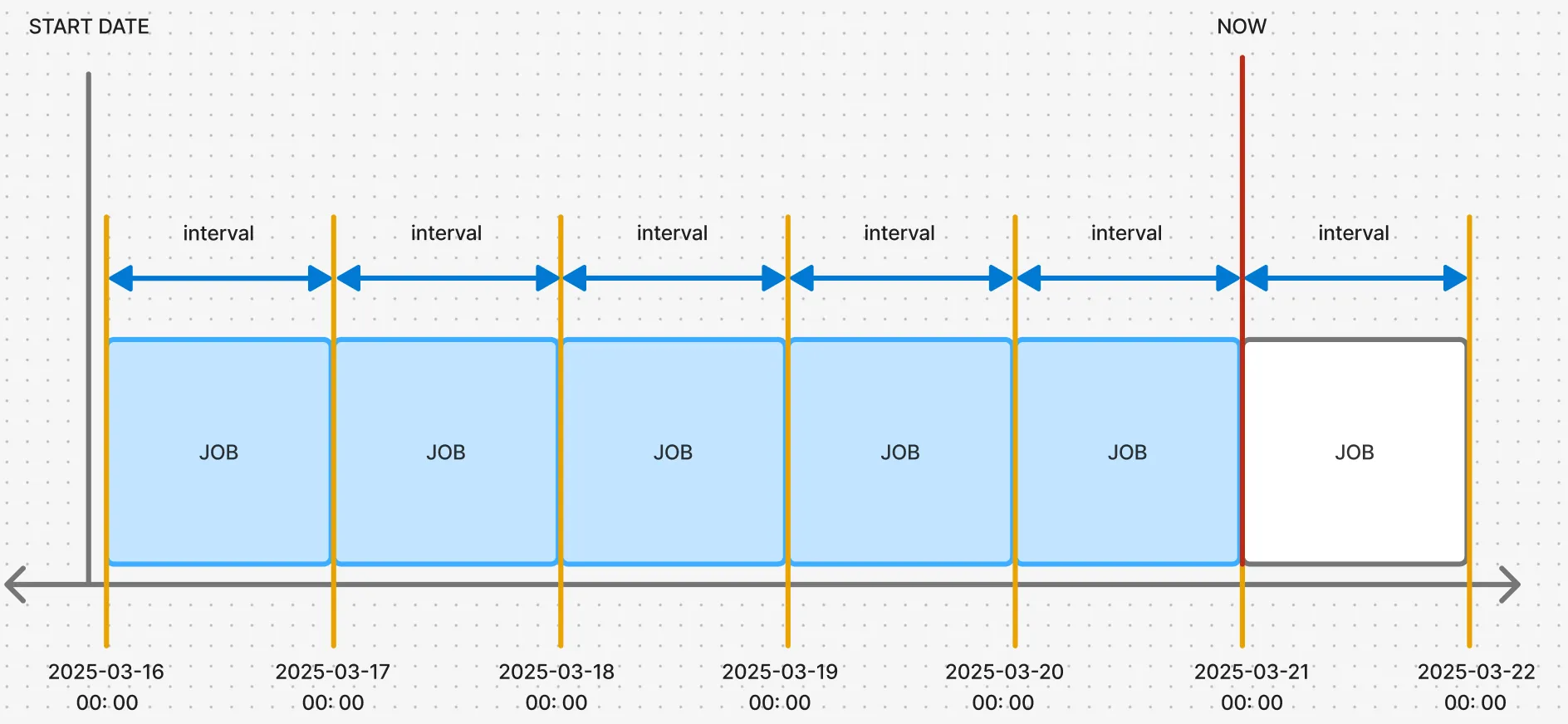
The diagram shows a schedule that runs at 00:00 on March 21st, processing data from the interval between 00:00 and 23:59 on March 20th.
When the job at the point marked “NOW” runs, a typical ETL task operates on a specific data interval. Therefore, for the job starting at 03-21 00:00, the target data interval is from 2025-03-20 00:00 to 2025-03-20 23:59.
In Airflow:
- The start of the data interval, 2025-03-20 00:00, is referred to as data_interval_start or the logical date.
- The end of the data interval, 2025-03-20 23:59, is referred to as data_interval_end.
ExternalTaskSensor
Airflow provides the ExternalTaskSensor to define dependencies between DAGs (Official Docs).
Dependencies are set using the following arguments:
external_task_sensor.ExternalTaskSensor(
external_dag_id, # upstream dag id
external_task_id, # upstream task id (job_id)
execution_delta # datetime.timedelta between the logical dates of downstream and upstream tasks
)
- My understanding is that since a cron schedule can trigger multiple job runs, external_dag_id and external_task_id alone are insufficient. You need to explicitly state how far apart in time your target job is from the current job, which is what execution_delta is for.
- execution_delta accepts a datetime.timedelta object. A positive value signifies the past, and a negative value signifies the future (e.g., **datetime.timedelta(days=1) refers to yesterday).
- The implementation calculates the timedelta from the downstream DAG’s perspective to the upstream DAG’s logical date. Therefore, downstream_dag.logical_date - upstream_dag.logical_date is passed as the value for execution_delta.
Implementation
To improve the existing external sensor algorithm to enable the calculation of execution_delta between any two cron objects, since every DAG has a cron schedule.
The development was based on the following assumptions (upstream and downstream DAGs/tasks are abbreviated as up and down):
nowcan be the execution time for bothupanddown.nowcan be the execution time fordownonly.nowcannot be the execution time foruponly.nowcannot be a non-execution time for bothupanddown.
Cases 3 and 4 were excluded as they are either unnecessary or impossible. The implementation only considers cases 1 and 2.
Case 1
This is when both DAGs are scheduled to execute at the current time and have a dependency on each other. Let’s use an example:
- Upstream DAG:
0 0 * * *# Runs daily at midnight - Downstream DAG:
0 0 */2 * *# Runs every two days at midnight
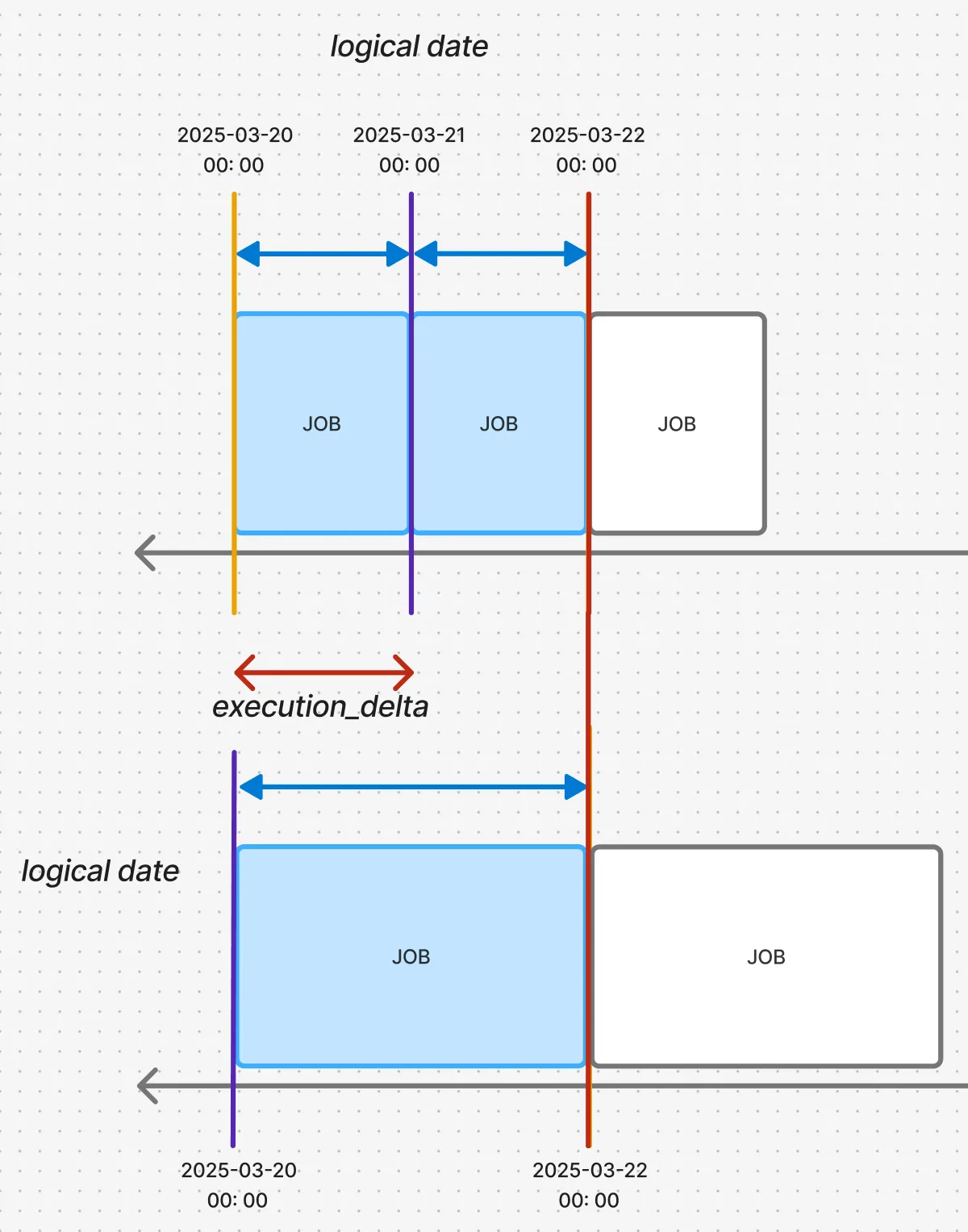 The top timeline represents the upstream DAG, and the bottom represents the downstream DAG. The execution times and logical dates are marked with red and purple lines, respectively.
The top timeline represents the upstream DAG, and the bottom represents the downstream DAG. The execution times and logical dates are marked with red and purple lines, respectively.
- In this case, the upstream DAG’s logical date is 2025-03-21 00:00, and the downstream DAG’s logical date is 2025-03-20 00:00. Therefore, the execution_delta is datetime.timedelta(days=-1).
- Semantically, this means the downstream DAG depends on an upstream job whose logical date is 1 day after its own logical date.
Case 2
This is when the downstream DAG is scheduled to run at the current time (now), but the upstream DAG is not.
-
This dependency is necessary for situations, where an hourly cron job uses daily dumped data. If the daily dump job runs at the same time, the hourly job must wait for it to complete.
- Upstream DAG:
0 6 * * *# Runs daily at 6:00 AM - Downstream DAG:
0 * * * *# Runs hourly
- Upstream DAG:
The top timeline represents the upstream DAG, and the bottom represents the downstream DAG. The execution times and logical dates are marked with red and purple lines, respectively. 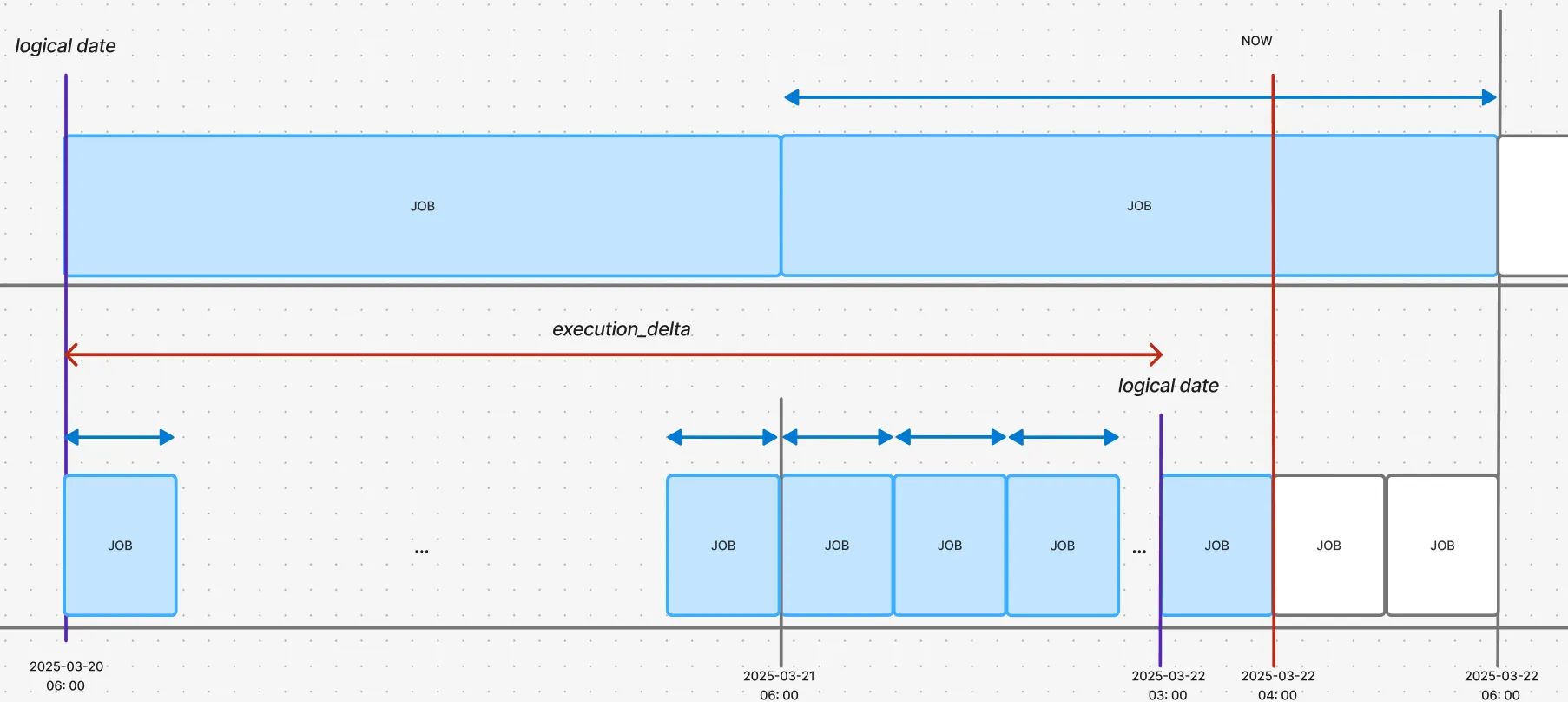
In this scenario, the hourly cron job running at “NOW” (March 22, 4:00 AM) uses the result of the daily dump that ran at March 21, 6:00 AM. The logical date for that daily dump job is March 20, 6:00 AM. Therefore:
- Upstream DAG’s logical date is 2025-03-20 06:00
- Downstream DAG’s logical date is 2025-03-22 03:00
The resulting execution_delta is datetime.timedelta(days=1, hours=21).
Additional Examples
- Condition
- Execution Time: 2025-03-21 06:00 (Friday)
- Example 1 (Case 1)
- Upstream DAG: daily cron (interval=1, hour=6)
- Downstream DAG: daily cron (interval=1, hour=6)
- Calculation
- Downstream DAG logical date = 2025-03-20 06:00
- Upstream DAG logical date = 2025-03-20 06:00
- execution_delta = 0
- Example 2 (Case 1)
- Upstream: daily cron (interval=1, hour=6)
- Downstream: days-of-week cron (days-of-week=[1,3,5], hour=6) (Mon, Wed, Fri)
- Calculation
- Downstream logical date = 2025-03-19 06:00
- Upstream logical date = 2025-03-20 06:00
- execution_delta = timedelta(days=-1)
- Example 3 (Case 2)
- Upstream: days-of-week cron (days-of-week=[2,4], hour=6) (Tue, Thu)
- Downstream: daily cron (interval=1, hour=6)
- Calculation
- Downstream logical date = 2025-03-20 06:00
- Upstream logical date: 2025-03-18 06:00
- execution_delta = timedelta(days=2)
- Example 4 (Case 1)
- Upstream: days-of-week cron (days-of-week=[1,3,5], hour=6) (Mon, Wed, Fri)
- Downstream: daily cron (interval=1, hour=6)
- Calculation
- Downstream logical date = 2025-03-20 06:00
- Upstream logical date: 2025-03-19 06:00
- execution_delta = timedelta(days=1)